The polarographic behaviour of salicylidenebenzohydrazide (SBH) at a dropping-mercury electrode was studied in aqueous Britton–Robinson buffers containing 40% ethanol. The polarograms consist each of one wave in acidic medium. The height of the wave decreases and its E½ shifts to more negative potentials with increasing pH until it diminishes completely at pH > 10.7. At pH values > 7.2 a second wave appears, the height of which increases with pH and becomes developed at pH values > 10.7. In acid solutions 4-electrons are consumed in the reduction of C[double bond, length half m-dash]N. The second wave is attributed to the reduction of salicylaldehyde which is formed from the hydrolysis of the hydrazide. The effect of pH on the limiting current and E½ as well as the reduction mechanism are discussed. The kinetic parameters of the electrode reaction are also determined.
Main navigation
- Main
-
About AAUP
Image
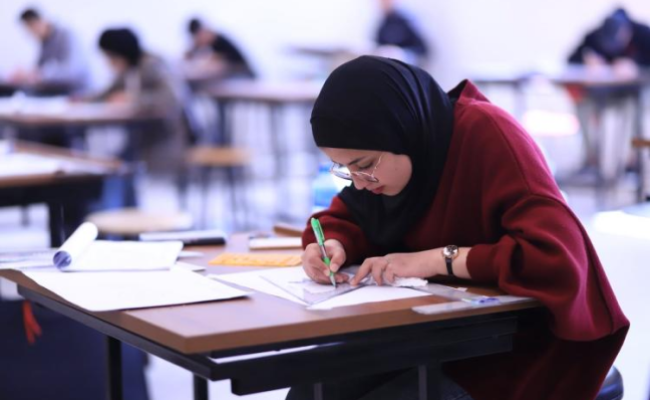


Give university
For those who wish to donate to the university, you can make your donations by filling out the donation form
-
Study
Image
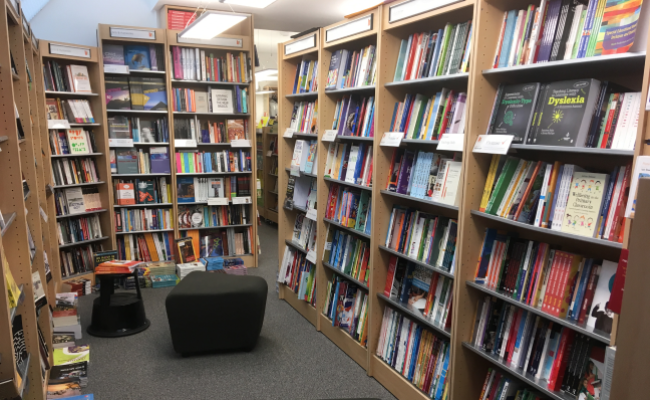


Arab American University Library
A distinguished library at the local and international levels by providing all electronic and paper information resources.
-
University life
Image
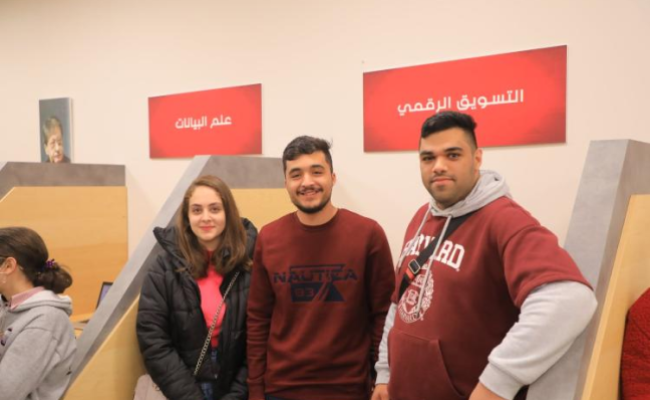

Inspiring success stories from the Arab American University
Success represents the pinnacle of persistence in the face of failure. So, these are the success stories we will share with you that reveal the path taken by some of our university’s graduates.
-
University centers
- Center for Research and Polling
- Center of Excellence for Climate Change and Environmental Technologies
- Conflict Studies Research Center
- Continuing Education Center
- Dental Center
- E-Learning Center
- Hassib Sabbagh Center of Excellence
- Heart Center
- Language Center
- Medical Center - Ramallah
- National Digital Transformation Center
- Prosthetics and Orthotics Factory
- Simulation Center
Image
Medical Rehabilitation Complex
-
Research
Image


Arab American University Awards
As part of the university’s efforts to support and encourage scientific research, there are a set of awards to encourage researchers to excel in their original and valuable scientific production
-
Media Center
Image


AAUP ACADEMIC CALENDAR
An agenda to show the the important dates such as semester dates, registration, exams, activities, events, and holidays.
