In this work, the X-ray diffraction, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and the spectral ellipsometry techniques are employed to investigate the structural, pseudo-optical and pseudodielectric properties of arsenic selenide thin films. The stoichiometric films which are prepared by thermal evaporation technique are found to prefer the amorphous nature of growth. While the pseudo-absorption coefficient spectra display strong absorption bands at 1.84, 1.81, 1.41 and 1.13 eV, the preferred pseudo-optical transitions happens within a direct forbidden energy band gap of 1.80 eV. In addition, the real part of the pseudodielectric spectra displays three strong resonance peaks at critical energy value of 2.33, 1.90 and 1.29 eV. Modeling of the imaginary part of the pseudodielectric constant spectra in accordance with the Drude-Lorentz approach resulted in the existence of six linear oscillators. The response of arsenic selenide to elliptically polarized light signals has shown that the films exhibit drift mobility, free electron concentration, and plasmon frequency values in the ranges of 0.21-43.96 〖cm〗^2/Vs, 1.90-58.0×〖10〗^19 〖cm〗^(-3) and 5.8-32.0 GHz, respectively. The optical conductivity parameters for As2Se3 film nominates it as promising candidates for the fabrication of tunneling diodes suitable for microwaves filtering up to 32.0 GHz and as thin film transistors.
Main navigation
- Main
-
About AAUP
Image
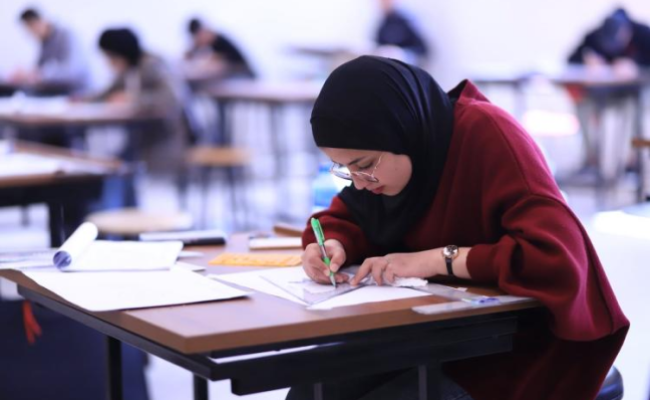


Give university
For those who wish to donate to the university, you can make your donations by filling out the donation form
-
Study
Image
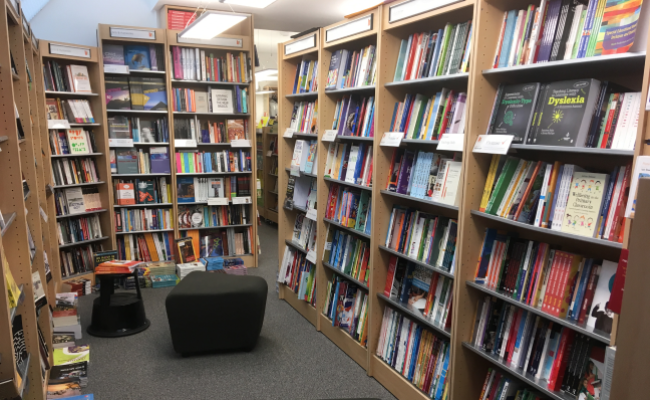


Arab American University Library
A distinguished library at the local and international levels by providing all electronic and paper information resources.
-
University life
Image
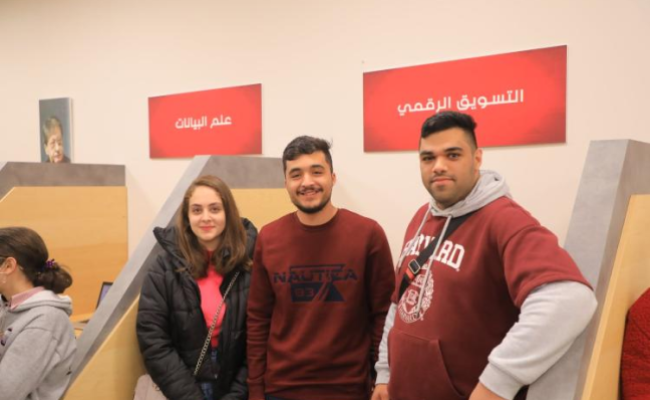

Inspiring success stories from the Arab American University
Success represents the pinnacle of persistence in the face of failure. So, these are the success stories we will share with you that reveal the path taken by some of our university’s graduates.
-
University centers
- Center for Research and Polling
- Center of Excellence for Climate Change and Environmental Technologies
- Conflict Studies Research Center
- Continuing Education Center
- Dental Center
- E-Learning Center
- Hassib Sabbagh Center of Excellence
- Heart Center
- Language Center
- Medical Center - Ramallah
- National Digital Transformation and Artificial Intelligence Center
- Prosthetics and Orthotics Factory
- Simulation Center
Image
Medical Rehabilitation Complex
-
Research
Image


Arab American University Awards
As part of the university’s efforts to support and encourage scientific research, there are a set of awards to encourage researchers to excel in their original and valuable scientific production
-
Media Center
Image


AAUP ACADEMIC CALENDAR
An agenda to show the the important dates such as semester dates, registration, exams, activities, events, and holidays.
