The voltammetric behavior of 5-nitrobenzimidazole was investigated using cyclic voltammetry and differential-pulse stripping voltammetry at bare glassy carbon (GC) electrodes and DNA-modified glassy carbon (DNA-GC) electrodes. A comparison between the current responses for the 5-nitrobenzimidazole at the modified DNA-GC and unmodified GC electrodes, it was showed that the DNA- modified electrode exhibits a significant enhancement of the voltammetric current response with a better peak shape. Optimization of the pre-concentration process at the DNA-modified surface led to a significant enhancement of the voltammetric current response and a better-defined peak shape. A linear relationship between the peak current and 5-nitrobenzimidazole concentrations was observed in the range 1.0–30.0 µM, with a slope a detection limit of 0.36 µM, with r = 0.998.
Main navigation
- Main
-
About AAUP
Image
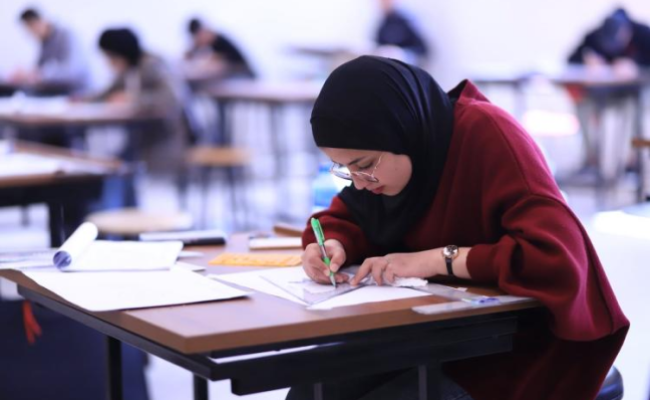


Give university
For those who wish to donate to the university, you can make your donations by filling out the donation form
-
Study
Image
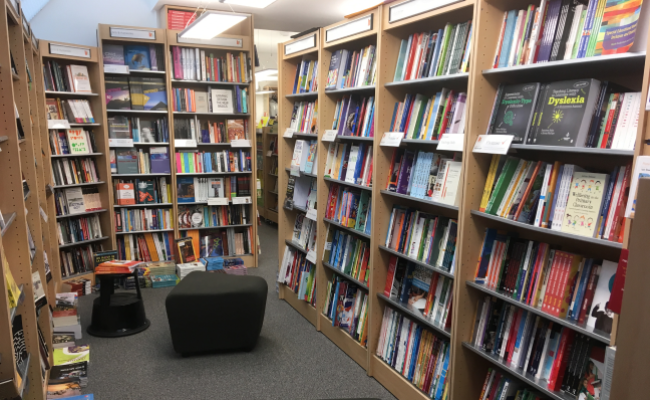


Arab American University Library
A distinguished library at the local and international levels by providing all electronic and paper information resources.
-
University life
Image
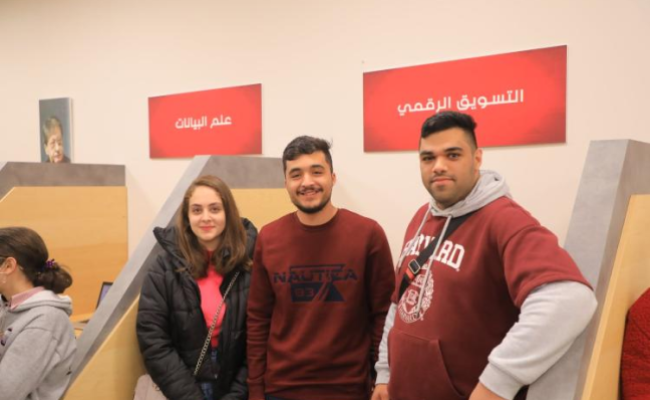

Inspiring success stories from the Arab American University
Success represents the pinnacle of persistence in the face of failure. So, these are the success stories we will share with you that reveal the path taken by some of our university’s graduates.
-
University centers
- Center for Research and Polling
- Center of Excellence for Climate Change and Environmental Technologies
- Conflict Studies Research Center
- Continuing Education Center
- Dental Center
- E-Learning Center
- Hassib Sabbagh Center of Excellence
- Heart Center
- Language Center
- Medical Center - Ramallah
- National Digital Transformation Center
- Prosthetics and Orthotics Factory
- Simulation Center
Image
Medical Rehabilitation Complex
-
Research
Image


Arab American University Awards
As part of the university’s efforts to support and encourage scientific research, there are a set of awards to encourage researchers to excel in their original and valuable scientific production
-
Media Center
Image


AAUP ACADEMIC CALENDAR
An agenda to show the the important dates such as semester dates, registration, exams, activities, events, and holidays.
