Surface texturing of transparent conducting oxides and plasmonic interfaces are two important techniques used separately in thin film solar cells to reduce reflection and enhance light-trapping. In this study, we merge the effects of Al:ZnO surface texturing and Ag nanoparticles (AgNPs) plasmonics in a single light-trapping interface to investigate their combined light trapping efficiency on a-Si:H thin film. Light scattered by this interface is optimized by placing a thin SiO2 spacer layer between AgNPs and a-Si:H absorber layer. Our results indicate that the AgNPs embedded in SiO2 significantly enhance absorption at energies close to the band gap of a-Si:H. Surface texturing by wet etching of Al:ZnO combined with AgNP produces the highest optical extinction of a-Si:H thin film at the band edge. Furthermore, the measured photocurrent in a-Si:H shows a clear increase not only at AgNPs resonance wavelength but over the entire wavelength range. (© 2015 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH Co. KGaA, Weinheim)
Main navigation
- Main
-
About AAUP
Image
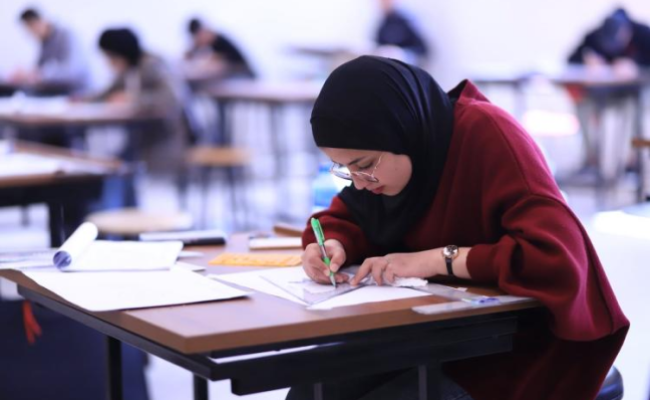


Give university
For those who wish to donate to the university, you can make your donations by filling out the donation form
-
Study
Image
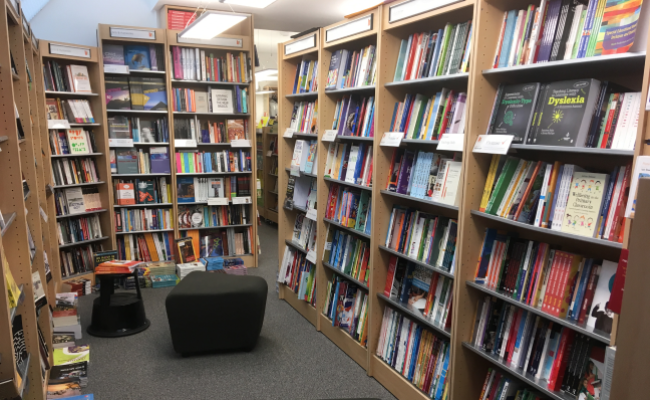


Arab American University Library
A distinguished library at the local and international levels by providing all electronic and paper information resources.
-
University life
Image
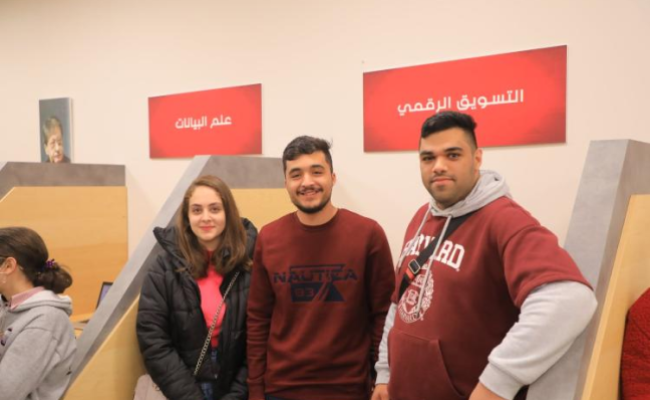

Inspiring success stories from the Arab American University
Success represents the pinnacle of persistence in the face of failure. So, these are the success stories we will share with you that reveal the path taken by some of our university’s graduates.
-
University centers
- Center for Research and Polling
- Center of Excellence for Climate Change and Environmental Technologies
- Conflict Studies Research Center
- Continuing Education Center
- Dental Center
- E-Learning Center
- Hassib Sabbagh Center of Excellence
- Heart Center
- Language Center
- Medical Center - Ramallah
- National Digital Transformation Center
- Prosthetics and Orthotics Factory
- Simulation Center
Image
Medical Rehabilitation Complex
-
Research
Image


Arab American University Awards
As part of the university’s efforts to support and encourage scientific research, there are a set of awards to encourage researchers to excel in their original and valuable scientific production
-
Media Center
Image


AAUP ACADEMIC CALENDAR
An agenda to show the the important dates such as semester dates, registration, exams, activities, events, and holidays.
