Albendazole is determined by differential-pulse adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetry at a hanging mercury drop electrode using the reduction peak of its copper(II) complex at −0.28V at an accumulation potential 0.0V vs. Ag/AgCl electrode. The optimum conditions of pH, accumulation potential and accumulation time were studied. The calibration graph for the determination of albendazole was linear in the range 3.0X10−8 - 9X10−7M with a relative standard deviation of 2.8%. The detection limit was 1.0X10−8M after 180s accumulation at 0.0V. The effect of common excipients and metal ions on the peak height of albendazole was studied. The presence of Cu2+ ions forms a stable complex with albendazole which is strongly adsorbed at the mercury electrode surface. The method was applied to the determination of the drug in commercially available dosage forms.
Main navigation
- الرئيسية
-
عن الجامعة
الصورة
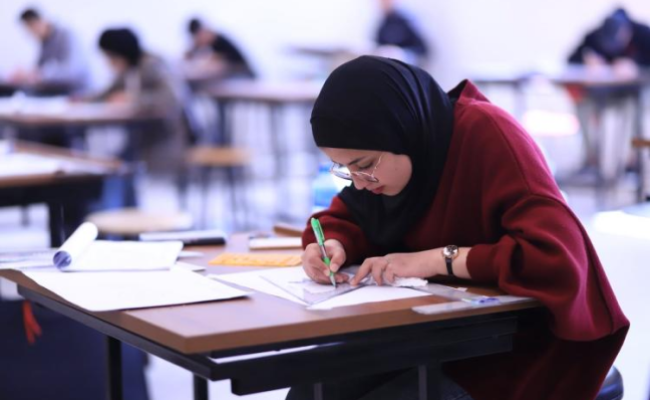


امنح الجامعة
لمن يرغب بالتبرع للجامعة، يمكنكم تقديم تبرعاتكم من خلال تعبئة النموذج الخاص بالتبرعات
-
الدراسة
الصورة
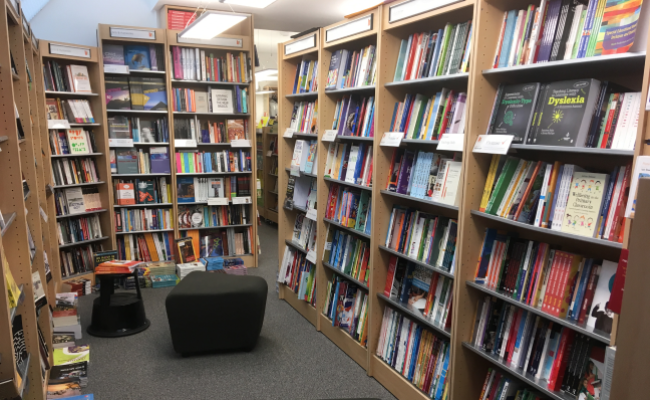


مكتبة الجامعة العربية الأمريكية
مكتبة متميزة على المستوى المحلي والعالمي من خلال توفير جميع اوعية المعلومات الالكترونية والورقية.
-
الحياة الجامعية
الصورة
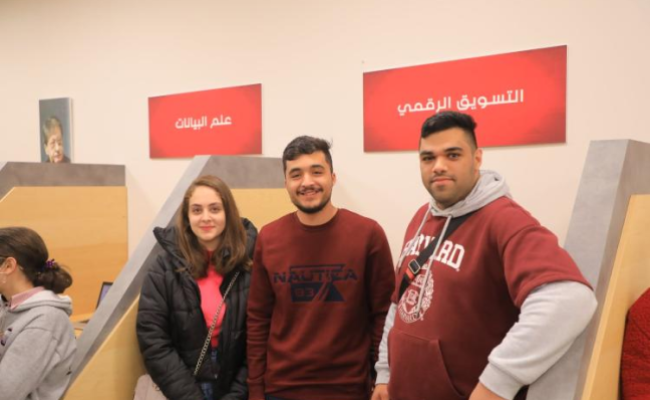

قصص نجاح ملهمة من الجامعة العربية الأمريكية
النجاح يُمثّل قمة الإصرار في مواجهة الفشل. لذا، هذا ما سنشاركه معكم من قصص نجاح تكشف الطريق الذي سلكه بعض خريجو جامعتنا.
-
مراكز الجامعة
- مركز البحوث و إستطلاع الرأي
- مركز تميز التغيير المناخي وتكنولوجيا البيئة
- مركز دراسات الصراع
- مركز التعليم المستمر
- مركز طب الأسنان
- مركز التعليم الإلكتروني
- مركز حسيب الصباغ للتميز
- مركز إنعاش القلب
- مركز اللغات
- المركز الطبي - رام الله
- المركز الوطني للتحول الرقمي
- مصنع الأطراف الصناعية والأجهزة المساعدة
- مركز المحاكاة
الصورة
المجمع الطبي التأهيلي الجامعي
-
البحث العلمي
الصورة


جوائز الجامعة العربية الامريكية
ضمن جهود الجامعة لدعم البحث العلمي وتشجيعه مجموعة من الجوائز لتشجيع الباحثين بالتميز بإنتاجهم العلمي الأصيل والقيِّم
-
المركز الاعلامي
الصورة


التقويم الأكاديمي الجامعي
أجندة لإظهار التواريخ المهمة مثل تواريخ الفصل الدراسي والتسجيل والامتحانات والأنشطة والفعاليات والعطل الرسمية.
