In this work, the effects of indium tin oxide (ITO) substrates on the structural, compositional, optical dielectric and optical conduction properties of arsenic selenide thin films are investigated. The As2Se3 films which are prepared by the thermal deposition technique under vacuum pressure of 10−5 mbar exhibit an induced crystallization process, improved stoichiometry, increased optical transmittance in the visible range of light and increased dielectric response in the infrared range of light upon replacement of glass substrates by ITO. The ITO/As2Se3 interfaces exhibit conduction and valence band offset values of 0.46 eV and 0.91 eV, respectively. The experimental optical conductivity spectra are theoretically reproduced with the help of the Drude–Lorentz approach for optical conduction. In accordance with this approach, owing to the improved crystallinity of the arsenic selenide, the deposition of As2Se3 onto ITO substrates increases the drift mobility value from ∼ 17.6 cm2/Vs to 34.6 cm2/Vs. It also reduces the density of free carriers by one order of magnitude. The ITO/As2Se3/C heterojunction devices which are tested as band filters which may operate in the frequency domain of 0.01–3.0 GHz revealed low pass filter characteristics below 0.35 GHz and band pass filter characteristics in the remaining spectral range.
Main navigation
- الرئيسية
-
عن الجامعة
الصورة
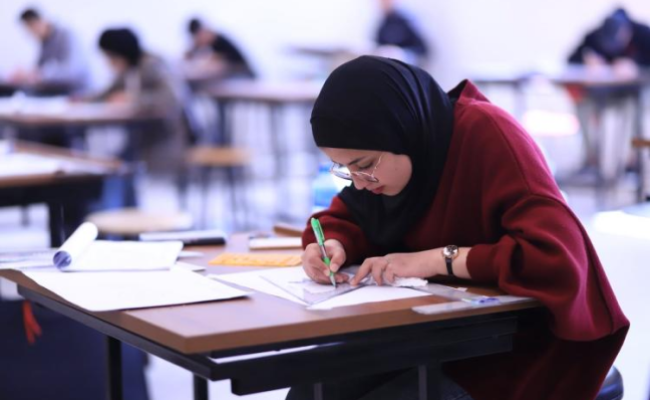


امنح الجامعة
لمن يرغب بالتبرع للجامعة، يمكنكم تقديم تبرعاتكم من خلال تعبئة النموذج الخاص بالتبرعات
-
الدراسة
الصورة
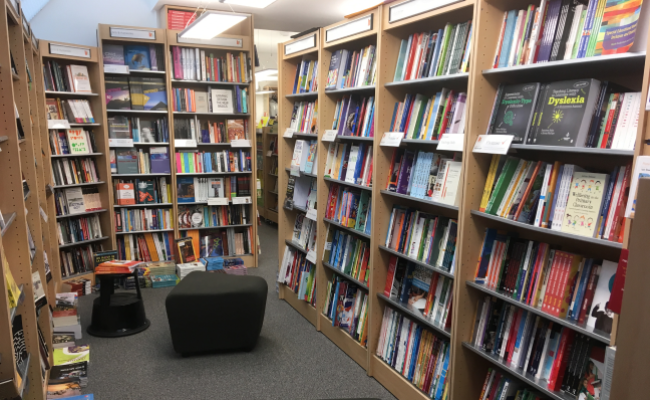


مكتبة الجامعة العربية الأمريكية
مكتبة متميزة على المستوى المحلي والعالمي من خلال توفير جميع اوعية المعلومات الالكترونية والورقية.
-
الحياة الجامعية
الصورة
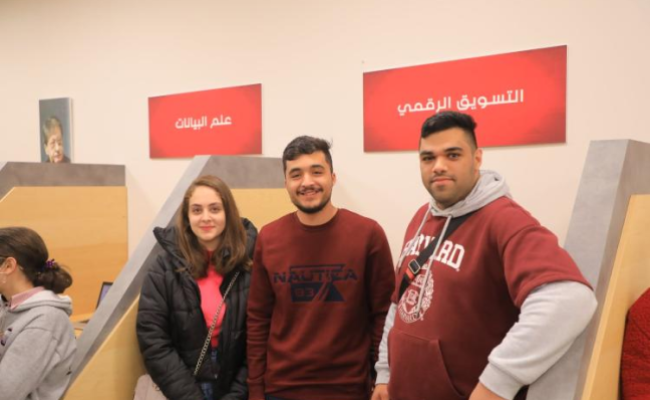

قصص نجاح ملهمة من الجامعة العربية الأمريكية
النجاح يُمثّل قمة الإصرار في مواجهة الفشل. لذا، هذا ما سنشاركه معكم من قصص نجاح تكشف الطريق الذي سلكه بعض خريجو جامعتنا.
-
مراكز الجامعة
- مركز البحوث و إستطلاع الرأي
- مركز التغير المناخي
- مركز دراسات الصراع
- مركز التعليم المستمر
- مركز طب الأسنان
- مركز التعليم الإلكتروني
- مركز حسيب الصباغ للتميز
- مركز إنعاش القلب
- مركز اللغات
- المركز الطبي - رام الله
- المركز الوطني للتحول الرقمي والذكاء الاصطناعي
- مصنع الأطراف الصناعية والأجهزة المساعدة
- مركز المحاكاة
الصورة
المجمع الطبي التأهيلي الجامعي
-
البحث العلمي
الصورة


جوائز الجامعة العربية الامريكية
ضمن جهود الجامعة لدعم البحث العلمي وتشجيعه مجموعة من الجوائز لتشجيع الباحثين بالتميز بإنتاجهم العلمي الأصيل والقيِّم
-
المركز الاعلامي
الصورة


التقويم الأكاديمي الجامعي
أجندة لإظهار التواريخ المهمة مثل تواريخ الفصل الدراسي والتسجيل والامتحانات والأنشطة والفعاليات والعطل الرسمية.
